|
| Statue of the Norman King Roger II of Sicily in a niche on the facade of
the royal Palace in the Piazza of Plebiscito, Naples. Carved in 1888. |
Detail of the mosaic with Roger II receiving the crown by Christ,
Martorana, Palermo. The mosaic carries an inscription Rogerios Rex in
Greek letters.
Roger II was the son of Count Roger de Hauteville, (see yesterday's blog.)
King Roger II of Sicily was born Dec. 22, 1095 in Sicily, and died Feb 26, 1154 in Sicily.
Roger II riding to war, from Liber ad honorem Augusti of Petrus de Ebulo, 1196.
Roger's tomb in the Cathedral of Palermo.
-----------------------------------
Here's what Wikepdia has to say about him:
Roger II (22 December 1095
[1] – 26
February 1154) was King of Sicily, son of Roger I of Sicily and
successor to his brother Simon. He began his rule as Count of Sicily in
1105, later became Duke of Apulia and Calabria (1127), then King of
Sicily (1130). It is Roger II's distinction to have united all the
Norman conquests in Italy into one kingdom with a strong centralized
government.
In
the early decades of the 11th century, Norman adventurers came to
southern Italy, initially to fight against the Saracens or the Byzantine
Empire. These mercenaries not only fought the enemies of the Italian
city-states, but in the following century they gradually became the
rulers of the major polities south of Rome
At the time of the
birth of his youngest son, in 1093, Roger I ruled the County of Sicily,
his nephew, Roger Borsa, was the Duke of Apulia and Calabria, and a
distant nephew, Richard II of Capua, was the Prince of Capua.
Alongside
these three major rulers were a large number of minor counts, who
effectively exercised sovereign power in their own localitites. These
counts at least nominally owed their allegiance to one of these three
Norman rulers, but such allegiance was usually weak and often ignored.
[2]
When
Roger I, Count of Sicily, died in 1101 the throne was assumed by his
young son, Simon of Hauteville, who himself died but four years later.
Reign
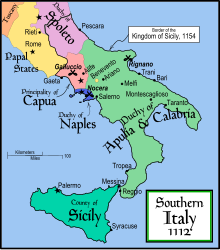
Southern
Italy in 1112 CE, at the time of Roger II's coming of age, showing the
major states and cities. Numerous smaller city-states, usually under the
suzerainty or vassalage of the larger states, are not shown.
The
border of the Kingdom of Sicily in 1154, at the time of Roger's death,
is shown by a thicker black line encircling most of southern Italy.
Rise to power in Sicily
On
the death of his elder brother, Simon of Hauteville, in 1105, Roger
inherited the County of Sicily under the regency of his mother, Adelaide
del Vasto. During this time the mother was assisted by such notables as
Christodulus, the emir of Palermo.
In the summer of 1110, he was visited by the Norwegian king Sigurd Jorsalfare on his way to Jerusalem.
In
1112, Roger attained his age of majority and began his personal rule,
being named "now knight, now Count of Sicily and Calabria" in a charter
document dated June 12, 1112.
[3]
In 1117, his mother,
who had married Baldwin I of Jerusalem, returned to Sicily, and Roger
married his first wife, Elvira, daughter of Alfonso VI of Castile and
his Moorish concubine or wife, Zaida.
In 1122, William II, the
Duke of Apulia and Roger's first cousin once removed, offered to
renounce his remaining claims to Sicily as well as part of Calabria.
Roger, in exchange, crossed the Straits of Messina to subjugate the
duke's vassal, Count Jordan of Ariano. In doing so, he penetrated the
Basilicata and took Montescaglioso.
 |
| Coronation mantle of Roger II |
Rise to power in southern Italy
When
William II of Apulia died childless in July 1127, Roger claimed all
Hauteville family possessions in the peninsula as well as the
overlordship of the Principality of Capua, which had been nominally
given to Apulia almost thirty years earlier. However, the union of
Sicily and Apulia was resisted by Pope Honorius II and by the subjects
of the duchy itself.
Royal investiture
The
popes had long been suspicious of the growth of Norman power in
southern Italy and at Capua in December, the pope [Pope Honorius] preached a crusade
against Roger, setting Robert II of Capua and Ranulf II of Alife (his
own brother-in-law) against him. After this coalition failed, in August
1128 Honorius invested Roger at Benevento as Duke of Apulia. The
baronial resistance, which was backed by Naples, Bari, Salerno, and
other cities whose aim was civic freedom, gave way. In September 1129
Roger was generally recognized as duke of Apulia by Sergius VII of
Naples, Robert of Capua, and the rest. He began at once to enforce order
in the duchy, where the ducal power had long been fading.
Upon
the death of Pope Honorius in February 1130 there were two claimants to
the papal throne. Roger supported Antipope Anacletus II against Innocent
II. The reward was a crown, and, on 27 September 1130, Anacletus' papal
bull made Roger king of Sicily. He was crowned in Palermo on the
Christmas Day 1130.
Peninsular rebellions
This
plunged Roger into a ten-year war. The famous Bernard of Clairvaux,
Innocent's champion, organized a coalition against Anacletus and his
"half-heathen king." He was joined by Louis VI of France, Henry I of
England, and the Lothair III, Holy Roman Emperor. Meanwhile southern
Italy revolted.
In 1130, the Duchy of Amalfi revolted and in 1131,
Roger sent John of Palermo across the Strait of Messina to join up with
a royal troop from Apulia and Calabria and march on Amalfi by land
while George of Antioch blockaded the town by sea and set up a base on
Capri.
[4] Amalfi soon capitulated.
In 1132, Roger sent
Robert II of Capua and Ranulf II of Alife to Rome in a show of force in
support of Anacletus. While they were away, Roger's half-sister Matilda,
the wife of Ranulf, fled to Roger claiming abuse. Simultaneously, Roger
annexed Ranulf's brother's County of Avellino. Ranulf demanded the
restitution of both wife and countship. Both were denied, and Ranulf
left Rome against orders, with Robert following.
First
Roger dealt with a rebellion in Apulia, where he defeated and deposed
Grimoald, Prince of Bari, replacing him with his second son Tancred.
Meanwhile, Robert and Ranulf took papal Benevento. Roger went to meet
them but was defeated at the Battle of Nocera on 25 July 1132. Roger
retreated to Salerno.
The next year, Lothair III came down to Rome
for his imperial coronation. The rebel leaders met with him there, but
they were refused help because Lothair's force was too small.
[5]
With the emperor's departure, divisions in his opponents' ranks allowed
Roger to reverse his fortunes. By July 1134, Roger's troops had forced
Ranulf, Sergius, and the other ringleaders to submit. Robert was
expelled from Capua and Roger installed his second son, Alfonso of
Hauteville as Prince of Capua. Roger II's eldest son Roger was given the
title of Duke of Apulia.
Meanwhile, Lothair's contemplated attack
upon Roger had gained the backing of Pisa, Genoa, and the Byzantine
emperor, each of whom feared the growth of a powerful Norman kingdom. A
Pisan fleet led by the exiled prince of Capua laid anchor in Naples
(1135). Ranulf joined Robert and Sergius there, encouraged by news
coming from Sicily that Roger was fatally ill or even already dead. The
important fortress of Aversa, among others, passed to the rebels, and
only Capua resisted under the royal chancellor, Guarin. On June 5,
however, Roger disembarked in Salerno, much to the surprise of the whole
mainland provinces. The royal army, split in several forces, easily
conquered Aversa and even Alife, the base of the natural rebel leader,
Ranulf. Most of the rebels took refuge in Naples, which was besieged in
July, but despite the poor health conditions within the city, Roger was
not able to take it, and returned to Messina late in the year.
Imperial invasion
In
1136, the long-awaited imperial army, led by Lothair and the duke of
Bavaria, Henry the Proud, descended the peninsula to support the three
rebels. Henry, Robert, and Ranulf took a large contingent of troops to
besiege the peninsular capital of the kingdom, Salerno. Roger remained
in Sicily, leaving its mainland garrisons helpless under the chancellor
Robert of Selby, while even the Byzantine emperor John II Comnenus sent
subsidies to Lothair. Salerno surrendered, and the large army of Germans
and Normans marched to the very south of Apulia. There, in June 1137,
Lothair besieged and took Bari. At San Severino, after the victorious
campaign, he and the pope jointly invested Ranulf as duke of Apulia
(August 1137), and the emperor then retired to Germany. Roger, freed
from the utmost danger, immediately disembarked in Calabria, at Tropea,
with 400 knights and other troops, probably mostly Muslims. After having
been welcomed by the Salernitans, he recovered ground in Campania,
sacking Pozzuoli, Alife, Capua, and Avellino. Sergius, terrified, was
forced to acknowledge him as overlord of Naples and sway his allegiance
to Anacletus: that moment marked the fall of an independent Neapolitan
duchy, and thereafter the ancient city was fully integrated into the
Norman realm.
Thence Roger moved to Benevento and northern Apulia,
where Duke Ranulf, although steadily losing his bases of power, had
some German troops plus some 1,500 knight from the cities of Melfi,
Trani, Troia, and Bari, who were "ready to die instead to lead a
miserable life." On 30 October 1137, at the Battle of Rignano (next to
Monte Gargano), the younger Roger and his father, with Sergius of
Naples, met the defensive army of Duke Ranulf. It was the greatest
defeat of Roger II's career. His son fought with courage, and Sergius
died honourably in battle, but Roger himself fled the field to Salerno.
It capped the meteoric career of Ranulf: twice victor over Roger.
Anacietus II died in January 1138, but Innocent II refused to reconcile
with the King.
In Spring 1138, the royal army invaded the
Principality of Capua, with the precise intent of avoiding a pitched
battle and of dispersing Ranulf's army with a series of marches along
sharp terrain. While the count of Alife lacked decision, Roger, now
supported by Benevento, destroyed all the rebels' castles in the region,
capturing an immense booty. Ranulf himself, who had taken refuge in
Troia, his capital, was killed by a malaric fever on 30 April 1139.
Later, Roger exhumed him from the Troian cathedral in which he was
buried and threw him in a ditch, only to later repent and rebury him
decently.
At this time, Sergius being dead, Alfonso was elected in
his place and together with his brother Roger, went off to conquer the
Abruzzi.
Consolidation of kingship
After
the death of Anacletus in January 1138, Roger had sought the
confirmation of his title from Pope Innocent. However, the pope wanted an
independent Principality of Capua as a buffer state between the Kingdom
of Sicily and the Papal States, something Roger would not accept.
[6] In the summer of 1139, Innocent II invaded the kingdom with a large army, but was ambushed at Galluccio on (22 July 1139),
[7]
southeast of present-day Cassino, by Roger's son and was captured.
Three days later, by the Treaty of Mignano, the pope proclaimed Roger II
as
rex Siciliae ducatus Apuliae et principatus Capuae. The boundaries of his
regno
were only later fixed by a truce with the pope in October 1144.
These
lands were for the next seven centuries to constitute the kingdoms of
Naples and Sicily.
In 1139, Bari, where during the wars of the
past year, 50,000 inhabitants had remained unscathed behind the massive
walls, decided to surrender: the
excellentissimus princeps
Jaquintus, who had led the rebellion of the city, was hanged together
with many of his followers, but the city avoided a sack. His execution
of the prince and his counsellors was perhaps the most violent act of
Roger's life.
While his sons overcame pockets of resistance on the
mainland, on 5 November 1139 Roger returned to Palermo to plan a great
act of legislation: the Assizes of Ariano an attempt to establish his
dominions in southern Italy as a coherent state. He returned to check up
on his sons' progress in 1140 and then went to Ariano, a town central
to the peninsular possessions (and a centre of rebellion under his
predecessors). There he promulgated the great law regulating all
Sicilian affairs. It invested the king and his bureaucracy with absolute
powers and reduced the authority of the often rebellious vassals. While
there, centralising his kingdom, Roger declared a new standard coinage,
named after the duchy of Apulia: the
ducat.

"The
Cappella Palatina, at Palermo, the most wonderful of Roger's churches,
with Norman doors, Saracenic arches, Byzantine dome, and roof adorned
with Arabic scripts, is perhaps the most striking product of the
brilliant and mixed civilization over which the grandson of the Norman
Trancred ruled" (EB1911).
Saracen arches and Byzantine mosaics complement each other within the
Palatine Chapel. The Palatine Chapel (Italian: Cappella Palatina) is
the royal chapel of the Norman kings of Sicily situated on the ground
floor at the center of the Palazzo Reale in Palermo.
Roger had now become one
of the greatest kings in Europe. At Palermo, Roger drew round him
distinguished men of various races, such as the famous Arab geographer
Idrisi and the Greek historian Nilus Doxopatrius. The king welcomed the
learned, and he practised toleration towards the several creeds, races
and languages of his realm. To administer his domain he hired many
Greeks and Arabs, who were trained in long-established traditions of
centralized government.
[8] He was served by men of nationality as dissimilar as the Englishman Thomas Brun, a
kaid of the
Curia, and, in the fleet, first by Christodulus and then George of Antioch, whom he made in 1132
ammiratus ammiratorum
or "Emir of Emirs," in effect prime vizier. This title gave way to the
English word admiral. Roger made Sicily the leading maritime power in
the Mediterranean.
A powerful fleet was built up under several
admirals, or "emirs", of whom the greatest was George, formerly in the
service of the Muslim prince of Mahdia. Mainly thanks to him, a series
of conquests were made on the African coast (1135–1153). Tripoli was
captured in 1146 and Cape Bona in 1148. These conquests were lost in the
reign of Roger's successor William and never formed an integral part of
the kingdom.
The Second Crusade (1147–1148) offered Roger an
opportunity to revive the attacks against the Byzantine Empire, the
traditional Norman enemy to the East. It also afforded him an
opportunity, through the agency of Theodwin, a cardinal ever-vigilant
for Crusade supporters, to strike up a correpondance with Conrad III of
Germany in an effort to break his alliance with Manuel I Comnenus. Roger
never went himself on an expedition against Byzantium, handing over the
command to the skillful George. In 1147, George set sail from Otranto
with seventy galleys to assault Corfu. According to Nicetas Choniates,
the island capitulated thanks to George's bribes (and the tax burden of
the imperial government), welcoming the Normans as their liberators.
Leaving a garrison, George sailed on to the Peloponnesus. He sacked
Athens and quickly moved on to the Ionian Islands. He ravaged the coast
all along Euboea and the Gulf of Corinth and penetrated as far as
Thebes, Greece, where he pillaged the silk factories and carried off the
Jewish damask, brocade, and silk weavers, taking them back to Palermo
where they formed the basis for the Sicilian silk industry. George
capped the expedition with a sack of Corinth, in which the relics of
Saint Theodore were stolen, and then returned to Sicily. In 1149,
however, Corfu was retaken. George went on a punitive expedition against
Constantinople, but could not land and instead defied the Byzantine
emperor by firing arrows against the palace windows. Yet the attack on
the empire had no enduring results.
The king died at Palermo on 26
February 1154, and was buried in the Cathedral of Palermo. He was
succeeded by his fourth son William. Roger II's elaborate coronation
cloak, later used by the Holy Roman Emperors, is now in the Imperial
Treasury (Schatzkammer) in Vienna. Roger is the subject of
King Roger, a 1926 opera by Polish composer Karol Szymanowski.
Family
Roger's
first marriage was in 1117 to Elvira of Castile, a daughter of King
Alfonso VI of Castile. They had six children:
- Roger (b. 1118 - d. 12 May 1148), heir, Duke of Apulia (from 1135), possibly also Count of Lecce;
- Tancred (b. 1119 - d. 1138), Prince of Bari (from 1135).
- Alfonso (b. 1120/1121 - d. 10 October 1144), Prince of Capua (from 1135) and Duke of Naples;
- Adelisa
(b. ca.1126? - d. aft.1184), Countess di Florenzia in her own right;
married firstly with Joscelin, Conte di Loreto, and secondly with
Robert, Conte di Loritello e Conversano.
- William (b. 1131 - d. 7 May 1166), his successor, Duke of Apulia (from 1148);
- Henry (b. 1135 - d. young).
Roger's second marriage was in 1149 to Sybille of Burgundy, daughter of Hugh II, Duke of Burgundy. They had two children:
- Henry (b. 29 August 1149 - d. young);
- Stillborn child (16 September 1150).
Roger's third marriage was in 1151 to Beatrix of Rethel, a grandniece of King Baldwin II of Jerusalem. They had a daughter:
- Constance
(b. posthumously 2 November 1154 - d. 28 November 1198), married with
the Emperor Henry VI, who became King of Sicily in his right.
Roger
also had several illegitimate children. One illegitimate daughter,
Marina, married the great admiral Margaritus of Brindisi. Another
illegitimate child, Simon, became the Prince of Taranto.
------------------------------------------------
Another source gives a bit of information about the succession of Roger II:
b. 1093-4 & d 1154 2/26, suc to the throne on the dth of his bro.
Simon 1105; but his mother governed during his minority. The antipope,
Anacletus II, on 1129 9/27, confirmed to him the strange title of 'King
of Sicily and Italy' which was modified in 1139 & confirmed to him
by Pope Innocent II upon their reconciliation. Consequently the 1st
Norman royal ruler of that Island, was: KING ROGER II of Sicily; and he
was an active, ewnergetic ruler, extending his domain in Italy, and
throughout adjacent islands of the sea; and altogether, his reign was
firm and prosperous. He was suc, before his dth. by his son WILLIAM I -
'the Bad,' who r. 1151-1166; and he, suc. by his son WILLIAM II, - the
'Good,' who r. 1166-1189, whose Queen Johanna, dau. of Henry of Anjou
and England, was childless. So, on his dth, the cr. passed to an
illegitimate gr. son of King Roger."
Underwood
----------------------------------
When I read these details for the third time, I noticed King Roger's son William I became ruler in 1151, while King Roger didn't die until 1154...is that strange sounding to you? It is to me. Perhaps he was sick and gave his son the crown...I wonder.
And still, where do these Norman/Sicilian Rogers connections come to my own family? Come back tomorrow on my blog (I'm doing genealogy all week...who knows, maybe all month! OK, probably not that long!)
I'm going to add this post to
Sepia Saturday, to share the ancient and confusing history of Italy in the time of it's dukedoms, and the strife over the Papal states...though I have very little knowledge of those histories. And I can sigh that the royalty of Sicily didn't continue to have my line, according to Ancestry at least, as I'll share tomorrow.)
Apologies for all the length of detail, which would probably make anyone snooze. But I just don't have any sepia photos related to this week's topic...